
Written by Becky Willson, Business Development & Technical Director
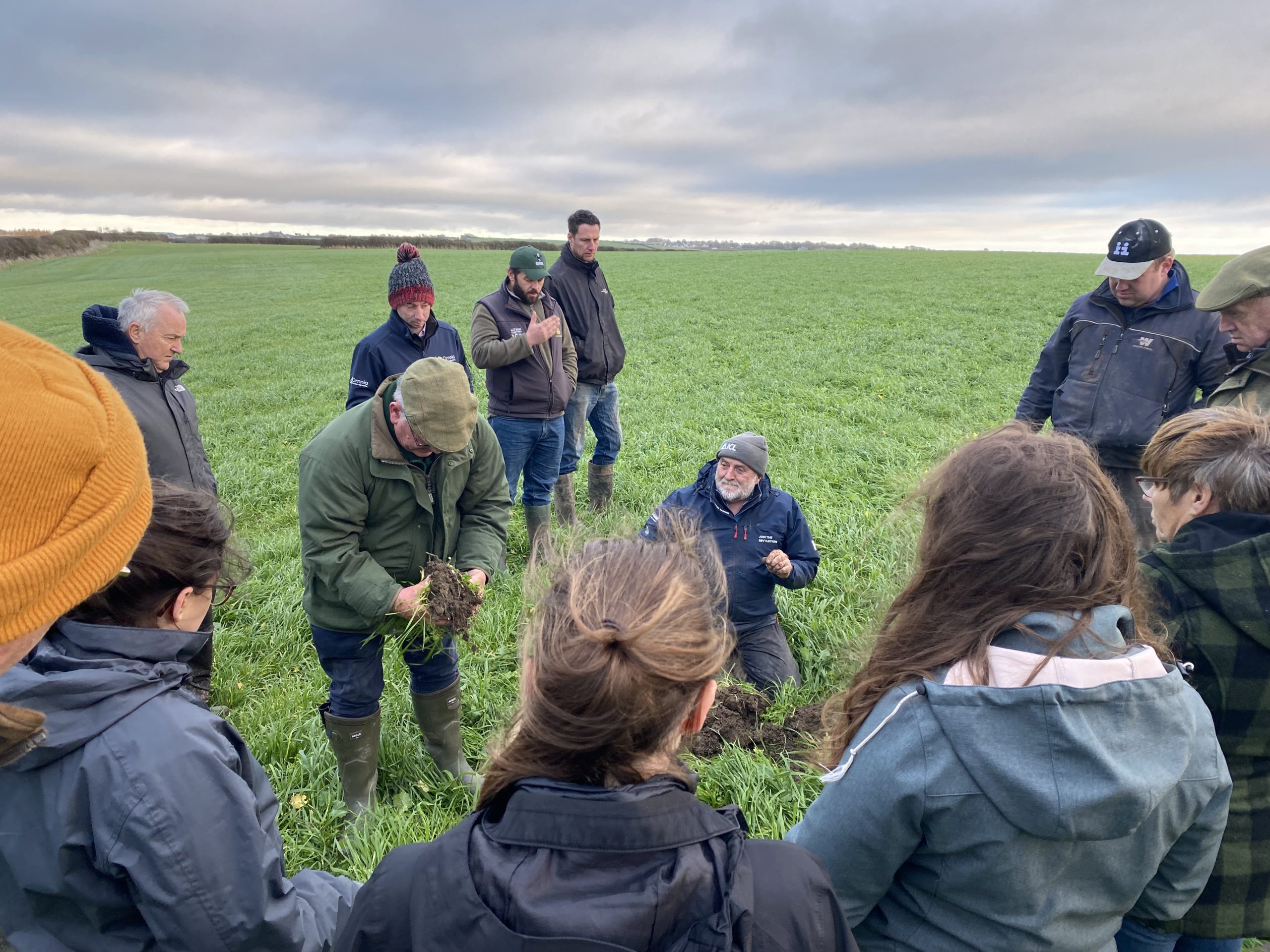
On a sunny day in September, farmers gathered at Rotmell Farm to take part in a farm walk with our Soil Farmer of the Year Winner from 2020. Thanks to funding from the AFN+ network, we have been able to revisit two farms this year to understand how their farm and management system has evolved since being awarded.

Rotmell Farm is 1000 ha, 800ha of which is unimproved pasture – encompassing heather, bracken and wet areas. The farm sits in the middle of the Tay Valley, and watching how water was moving through the landscape formed a key part of the decision to adapt the management of the farm to focus on soil health and water holding capacity. In order to achieve this the grazing management system was adapted in 2015/6 to include subdividing paddocks and starting to move stock. Since this time the farm has continued to evolve its management style until now where the primary driver for the farm is to use the stock to maximise carbon and nutrient cycling across the farm.
Alex explained:
I had thought that the moment that we started putting in fencing, subdividing, moving stock and going into taller covers and rotational grazing that we could balance saturations of key nutrients and achieve a system where no inputs were required. We’ve built organic matter and are growing pasture, but the system needs to be continuously managed and adapted to try and achieve that balance. I now regard grazing as an art form.

The event started with a session in the barn to understand the evolution of the system and the key principles that the farm uses to drive performance. A key driver over the last couple of years for Alex has been understanding total nutrition and the ability to balance nutrients to enable optimal soil and biological health. This has involved implementing in depth soil analysis to understand the balance of key nutrients within the soil and intensive observation of plant and animal performance to start to understand how they are working together. This has included a focus on calcium as the driver for improving structure, oxygen levels in the soil, grass production and carbon cycling.
The whole farm is set up for total nutrition. We are trying to get the biology working to grow high Brix grazing grass to feed to stock, to sell nutrient dense meats and other products into the local market.
The farm sells honey, eggs, and beef locally where the ability to connect the farm with the produce is valuable and helps to cement the farm as part of the local community and allowing them to identify with the produce and where it comes from.
Alex has adapted his grazing system to encourage more diversity in the leys and to graze taller residuals. He sees far greater value in the hoof impact through trampling than the grazing; when the animals are put into taller covers, they graze the plants higher up and don’t graze the base of the plant, which leads to the carbon rich material being returned to the soil, cycling that carbon to feed the biology. The intensiveness of movement of the stock helps to get the carbon back down into the soil. The tightness of grazing takes away selection of grass.
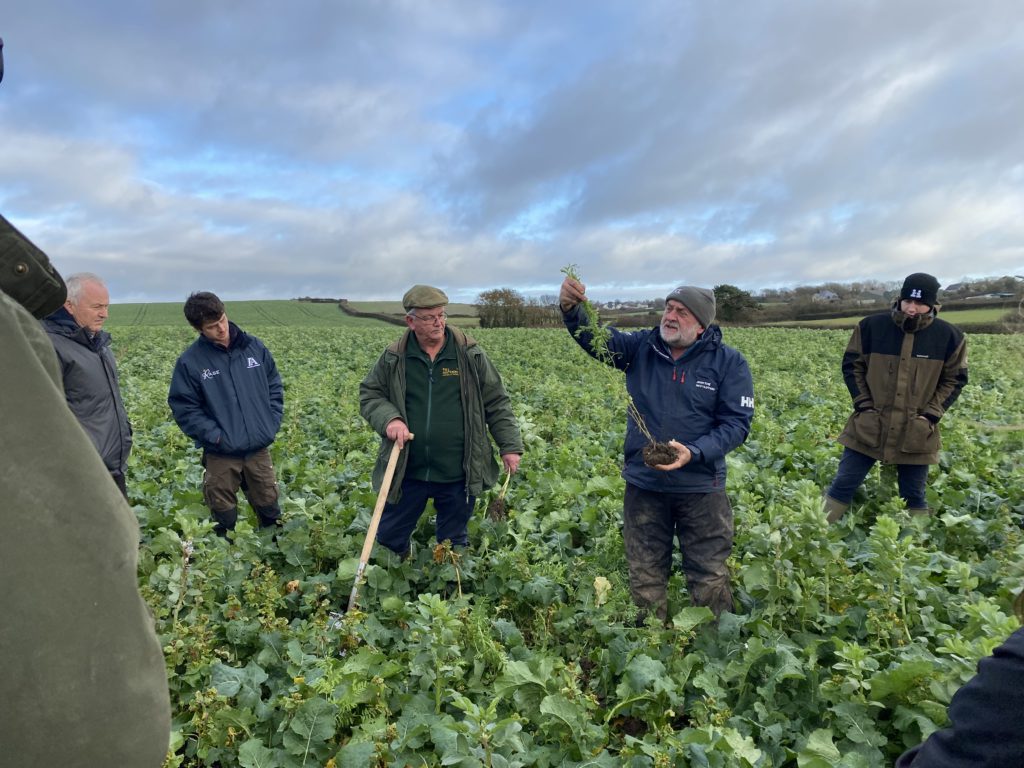
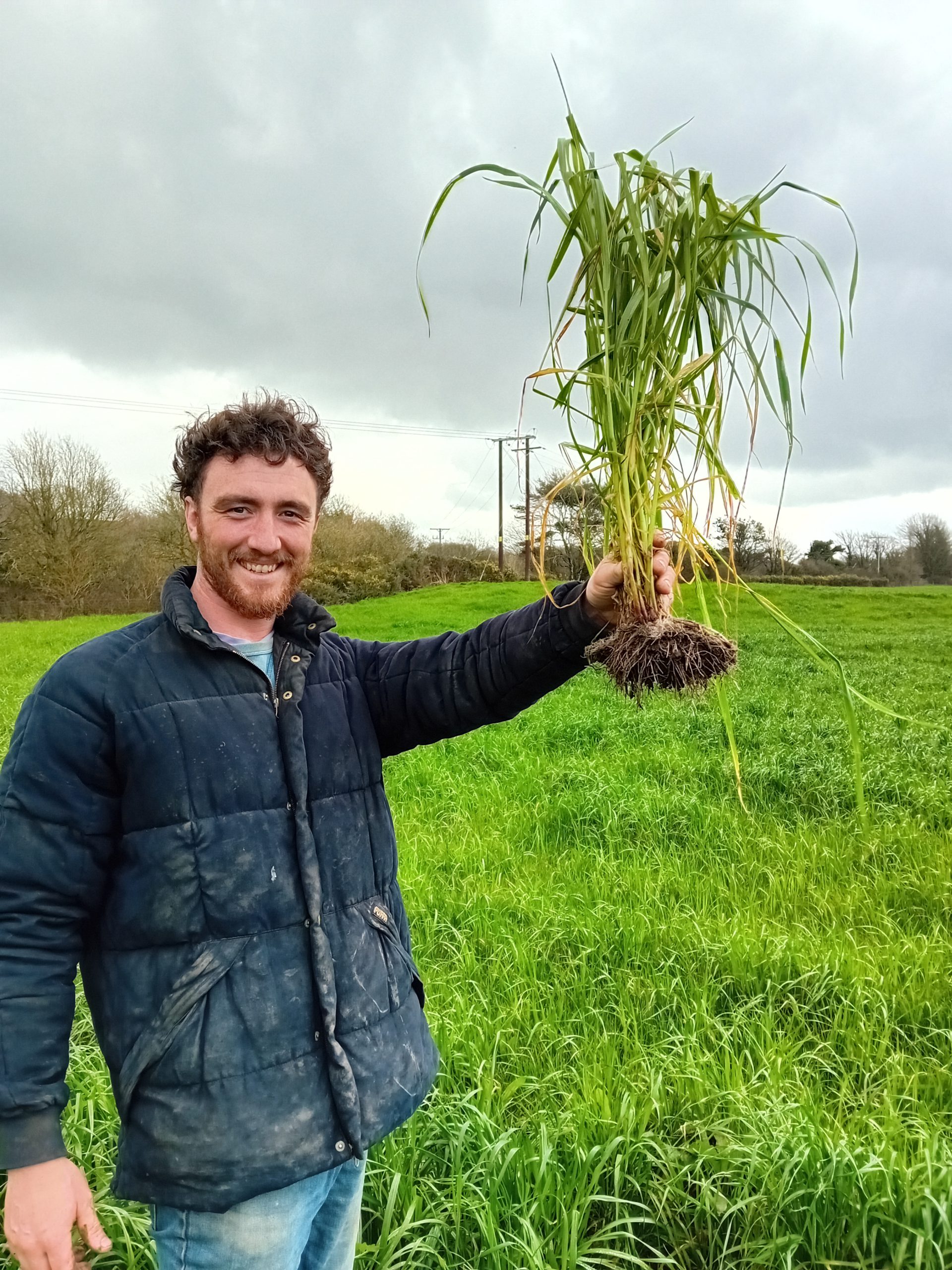
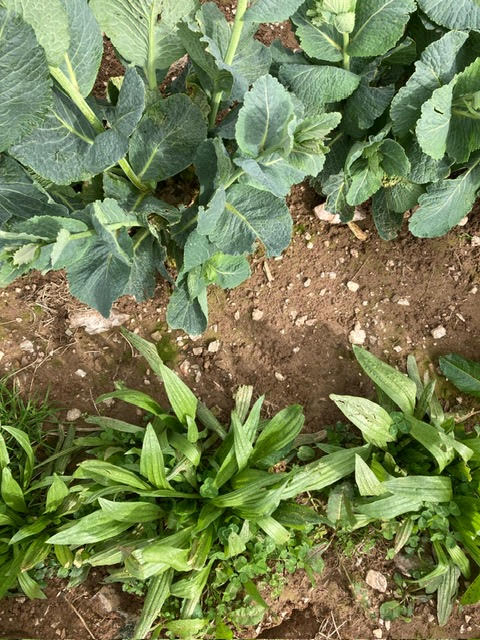
The first field that we went to see has been used as an experimental field to look at species mixes. Alex researched different grass mixes and has returned to a mix that was common in the 1880s which can be used to improve poorer land. The field had been forage rape previously with lambs grazing the aftermath. The field was then disced and the new ley was broadcast, rolled in and then left. It has just had its third grazing, having been grazed with sheep 8 weeks after sowing to encourage it to tiller in late July. It was then grazed with a mob of about 65-70 cattle to break the parasite window and then had a group of 200 ewes with twin lambs. Every time seeds are sown they are mixed with vermicast, humates and fine lime which encourages biological activity around the seeds and ensures the seed has everything it needs to get going.
Alex really sees the importance of a high seed rate which allows for a thick and vigorous sward but also helps to maximise the value of trampling. He is aiming for 285 plants per m2 and has seen this work well higher up the farm where it is increasing the density of grass and reducing coverage of moss.
The animals have adapted well to the changing system. All the stock are out all year round, there is no housing. Bales are put out for the winter, with the aim being to set up blocks to shift the cattle every two to three days on a self feed basis. The type of cow has changed as the system has evolved; the animals that cope better in this system are slightly smaller framed and carry flesh. The cows need to be at 350kg at 15 months in order to allow them to calve at 2 years old at around 450kg in the middle of April outside. Cattle are weighed and recorded regularly to monitor live weight gain and body condition and FEC tested every 90-100 days to monitor worm burdens. The sheep are also weighed regularly to provide insight into which animals and genetics are coping with the system. The sheep are supplemented with rock salt and minerals depending on the pasture and soil analysis.
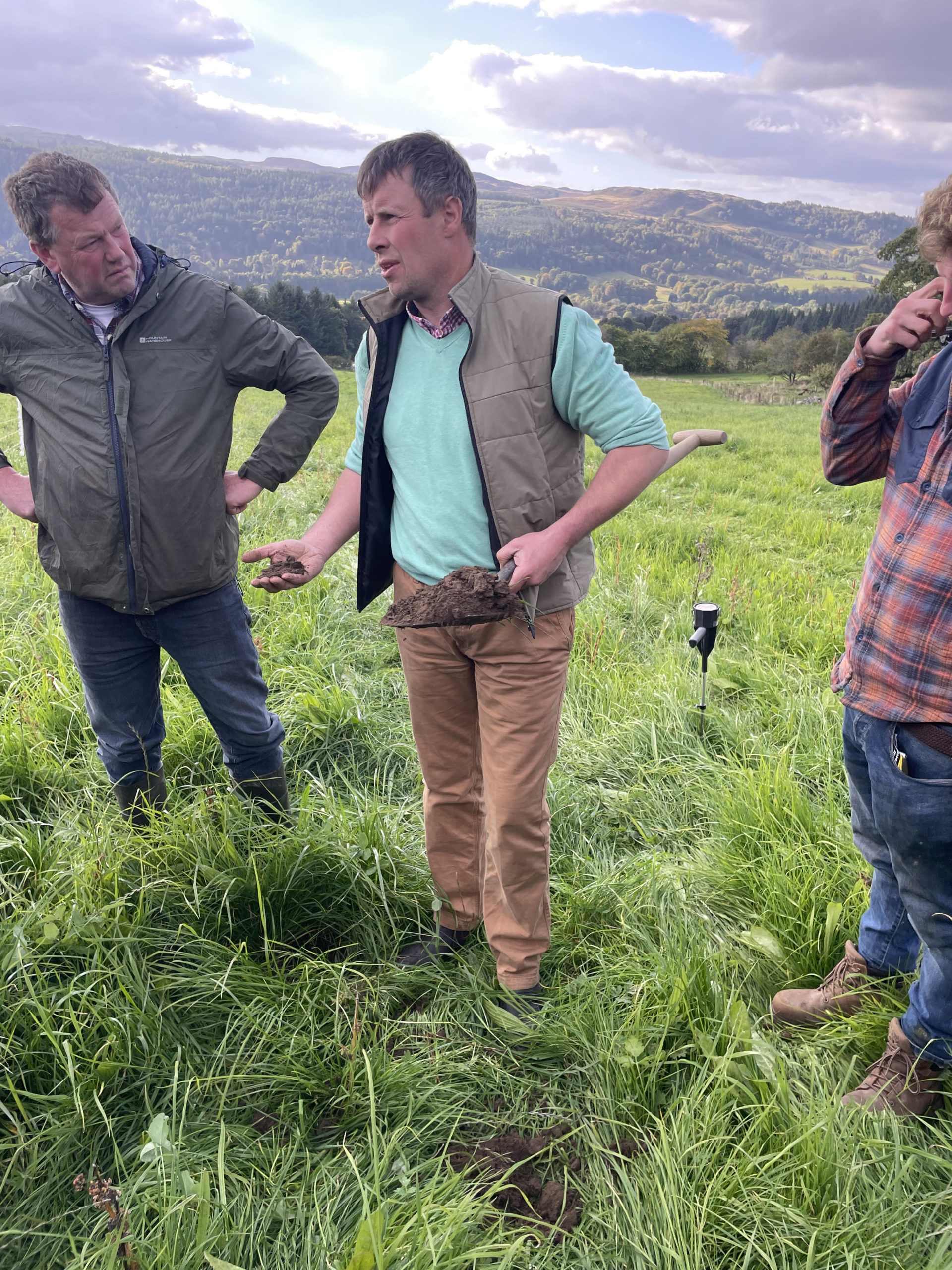
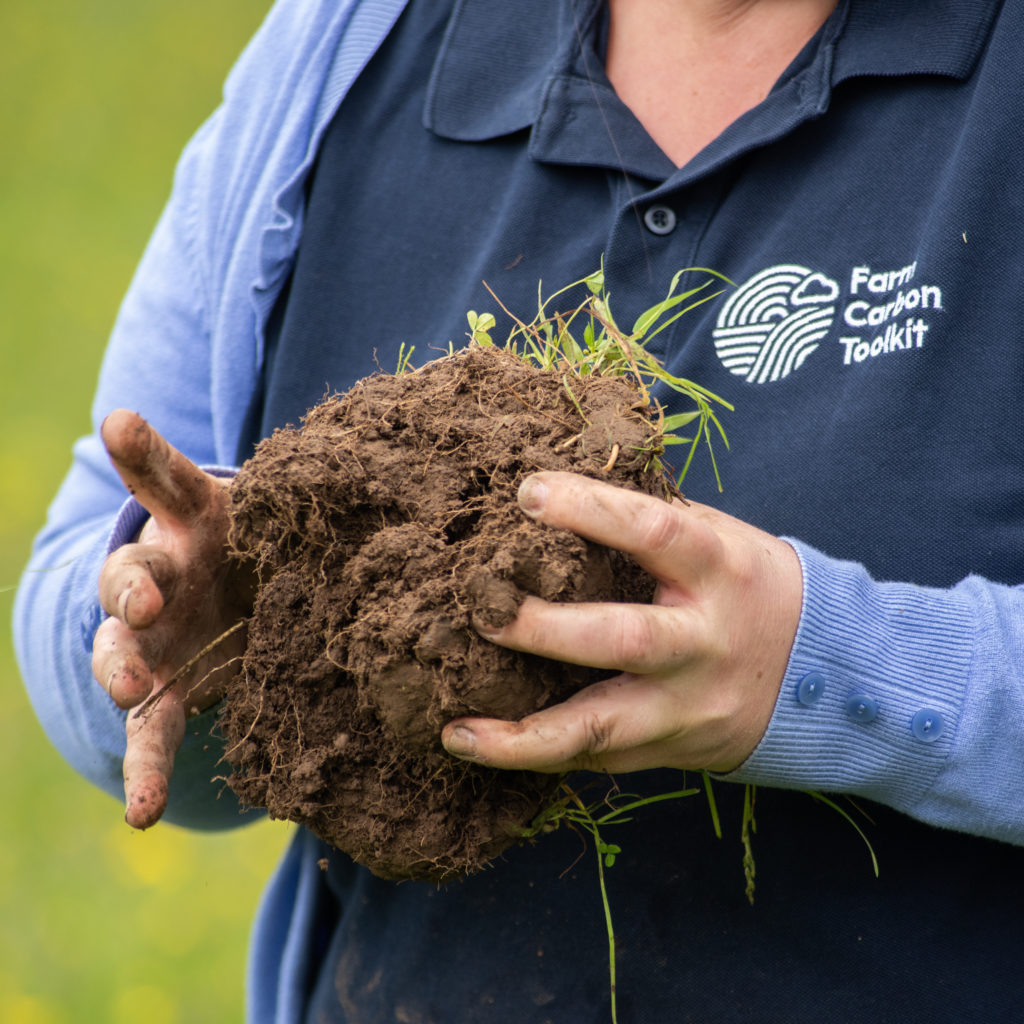
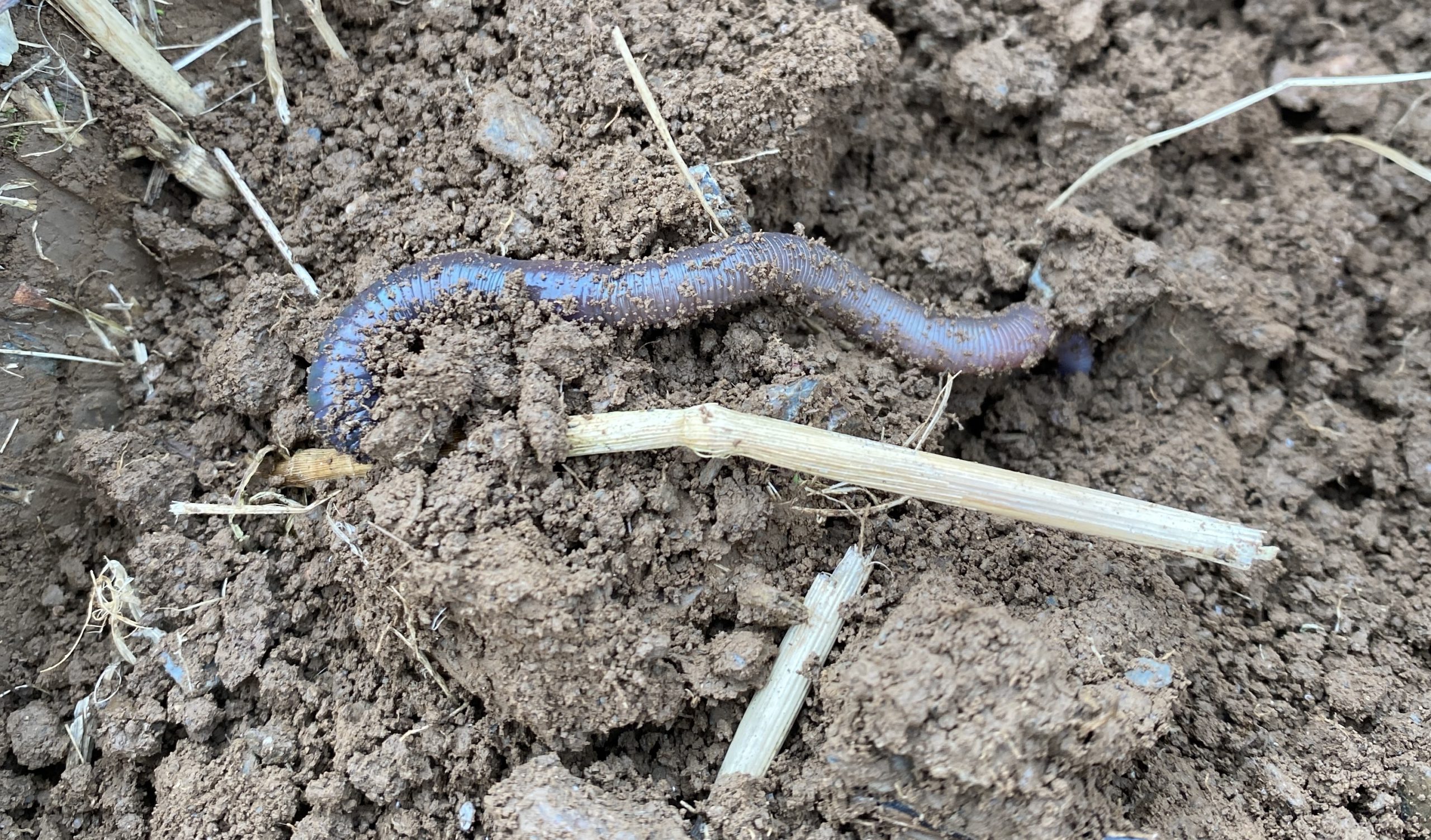
It wouldn’t be a soil farmer walk without a group of farmers standing over a soil pit and looking at the impact of the management changes on the soil. Alex has seen changes in soil health, since making the early transition to rotational grazing, however over the last couple of years has been focussing on enabling the biology to thrive and optimising nutrient cycling and the interaction between the soil and the plant roots. As such, two key assessment methods have been useful to show progress which have been the penetrometer and Brix assessments.
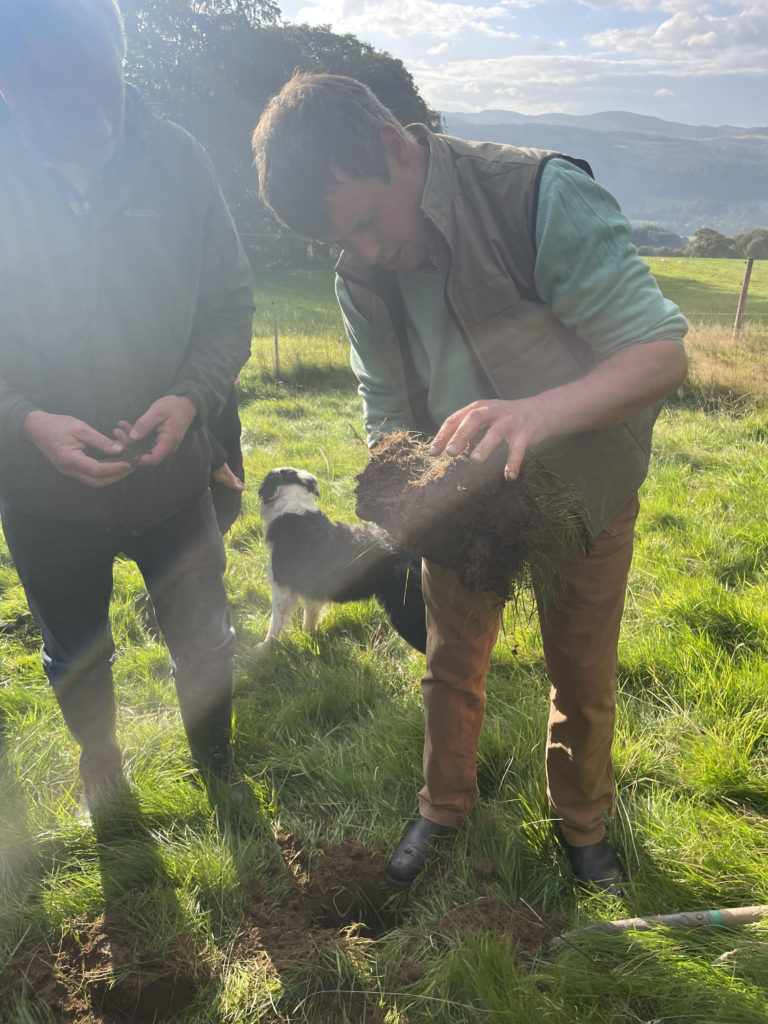

I started to get really excited about Brix readings a few years ago, and then really clocked onto it last year. I realised that the taller the plant got the Brix reading grew and grew, we started with 3’s and 4’s, as the covers got to boot stage readings got to 9’s and 10’s which was really exciting. This year, the penetrometer has been a useful tool, the pressure readings had been 250’s and 300 PSI and now we are down to 150, and I think that once we have psi’s of 150 then we are getting oxygen into the soil. We can send soil off to the lab for analysis, but how the soil is structured is a reflection of our management.
If we find fields that are compacted, I’ll skip them and give them 120 days rest rather than 60 days. We have stopped treating the whole farm as one block and looked at what the field needs and how we can optimise root architecture and plant diversity. Its important to us that every grazing experience is positive. We want to get to the point where we don’t need to apply anything, although we aren’t there yet. I’m not totally against applying anything, we need energy in the system and if the soils are tight, then we aren’t at optimal soil function, but the aim is to get to the point where we can target nutrition based on soil and plant need
Due to the nature of the farm and that 85% of the farm is hill areas, a key challenge for Alex has been to manage these areas in a way which can control the bracken ingress. He has been managing these areas in order to build capacity higher up, so that the in bye ground can be managed in a way to provide longer recovery periods.
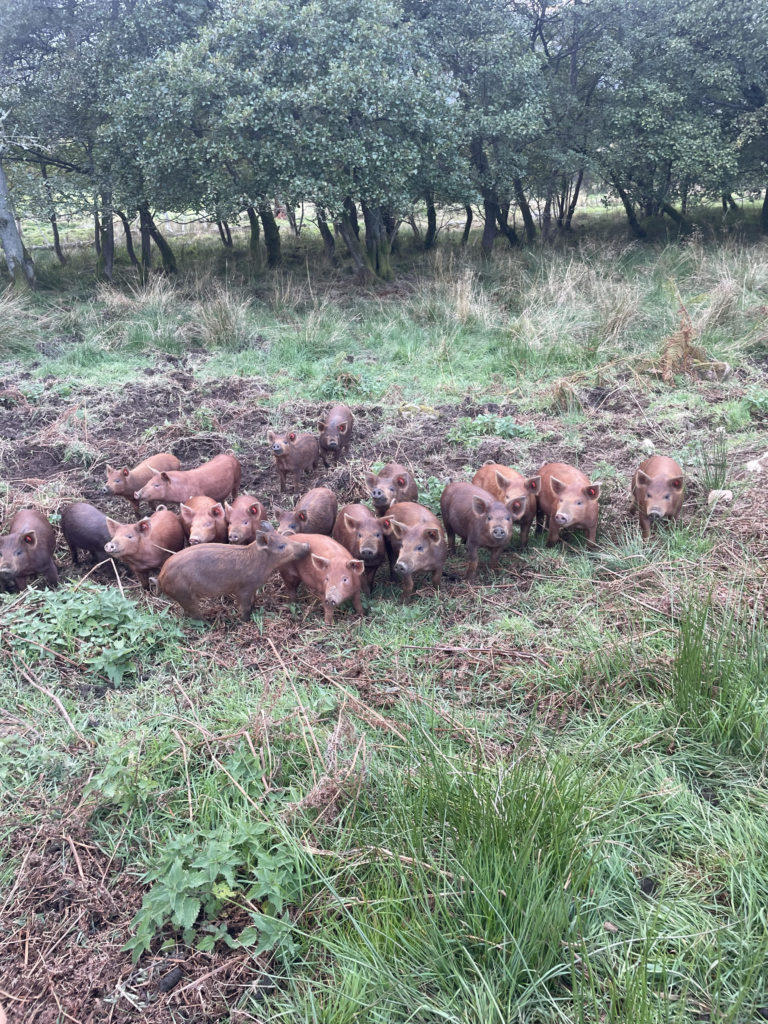
If I don’t keep enough stock to get on top of the bracken, I will lose the whole farm to it. We only have 8-10 weeks to influence on that plant when it is above the ground, the other part of the year it is below the ground. We have implemented a grazing system which is intensively extensive, really hard hitting when we are there – in the summertime we are moving cattle 4 times per day, but then really long recovery periods. Which allows us to knock the top cover of the plant back but not doing enough to impact the biology and chemistry of the plant – which is why we have just brought pigs onto the farm.
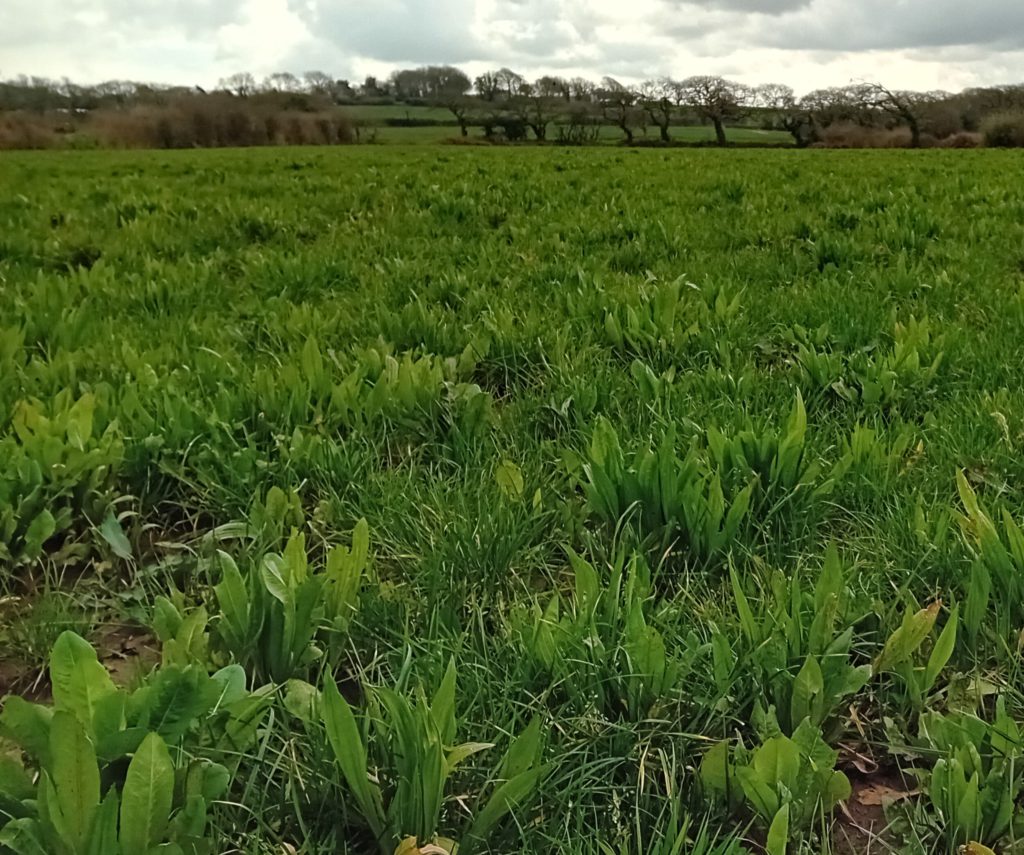
Where this has been implemented, the results have been remarkable. Where the bracken has been managed in this way, the pasture regrowth has been diverse – clovers, vetches and grasses alongside yarrow and red clover are now starting to emerge due to the management system. Although bracken in a challenge, Alex also sees the benefits of it when it is controlled as it is mobilising a lot of potassium around the system which can then be used to support the pasture regrowth. The management of these areas is crucial, where extensive management is leading to the development of these bracken areas,
The base geology between our unimproved and improved land is exactly the same, so the potential to increase output on that land is vast. The more I think about it, the more I think that soils don’t want to be extensively managed, they want to be intensively managed with long recovery periods. We produce a lot of disturbance and then get off it to let it recover.
The group then went to look at the pigs, the new tool in the bracken control strategy! The aim with the pigs is that their rooting activity will help to chew the roots of the bracken up and add manure to aid nutrient cycling. Following the pigs activity the area will then have seed broadcast to increase forage production. The pigs will also be moved into higher areas to help with the bracken control.

The final stop on the walk was at some slightly higher country. The field had been soil sampled and the results had shown good levels of organic matter but suppressed levels of biological activity. As such, Alex is conducting some trials looking at the efficacy of spreading fine lime as a way to improve the calcium content of the soil and enhance the biological activity. Analysis shows that there is most compaction on the farm in the in bye fields, higher up there is less compaction but lower pH’s and less biological activity; as such if we can grow more feed higher up then less forage is required. The farm is using half as much feed as they used to since transitioning to the system. The grass used to be very thatch dominated but there is now an increase in clovers and plantains starting to appear.
Alex explained his change in thinking to manage for what you want rather than what you want to control.
I was so transfixed about managing bracken, I forgot to manage the grass. So by managing the grass, I build the quality nutrition and manage the soils to get the system working, then the pastoral density comes and will deal with the bracken.
To finish the walk questions turned to what next? Alex has spent the last 6 years gathering data, digging holes and persisting to pull it all together. So for the future, he thinks that the big changes have been done, its more about being observational and tweaking the system to optimise biology.
Grass is the most undervalued crop and so we are starting to put it in through the introduction of the new leys. We aren’t carrying more livestock but we are spending a lot less money. Its taken me 10 years to understand how to manage this ground. The failures have been too high- to learn about this we have to get some of it wrong, I’ve never had a year yet where we have got everything right but that is how we learn. Now its time to deliver what we know will work and to drive that system we need nutrition. We’ve been funded to experiment and now the system has to deliver.
Our sincere thanks to the Alex and the team at Rotmell for a fascinating afternoon that gave everyone plenty to think about.





























Recent Comments