
by Liz Bowles, CEO
Groundswell this year was as exciting as ever, with so many excellent sessions and people to catch up with and meet for the first time.
There was much interest in how farmers and growers can benefit from the new markets for carbon, biodiversity net gain and nutrient neutrality to name but three, but to my mind, there was far less attention on how the sector can actually reduce the emissions associated with producing food itself.
For me, this is critical as we have to find a way to reduce the greenhouse gases we push into our atmosphere, as well as removing some of the historical emissions already there, if we are to reduce the worst impacts of climate change.
There is, however, a central question for our food system which is: What level of emissions are inevitable from the production of food which is essential for humanity? The Climate Change Committee has come up with a view on this in their 2020 UK agricultural policy for net zero report, which suggests a road map for saving 64% in the annual emissions from agriculture compared to 2017 levels when UK agriculture was responsible for around 58 MtCO2e (12% of total UK emissions). On closer inspection of the figures though, the actual savings in emissions from agriculture are set at around 21 MtCO2e / year, with the remaining savings to come from forestry, changes to our diet and the production of energy crops instead of food.
This is set out below:
The specific actions suggested for each of these areas are set out below:
- Tree planting on 30,000 hectares per year
- Use 10% of UK farmland for agroforestry (no distinction made between agroforestry and hedgerows)
- Restore at least 55% of peatland area by 2050. (For lowland peat lands this means rewetting or paludiculture to reduce emissions and for uplands this means rewetting).
- Increases in low-carbon farming practices for soils and livestock (no detail provided)
- Increase the area of farmland devoted to energy crops to 23,000 ha per year
From this list, the low carbon farming practices interest me in terms of how their adoption will enable an annual reduction of 10MtCO2e per year to occur (~25% of 2022 UK agricultural emissions). At Farm Carbon Toolkit we work directly with farmers and growers to adopt these practices and changes to current management processes. Typically the areas to focus on include:
- Planting cover crops
- Changing crop rotation
- Transitioning to no/min till where possible
- Growing new crops
- Integrated pest management
- Adopting rotational grazing
- Planting herbal leys
Across all these practices, there should be a focus on reducing the use of artificial nitrogen fertilisers and purchased livestock feed (especially those including imported ingredients) as both these inputs carry a high level of associated emissions.
Many of these practices can also be considered to be part of the suite of “regenerative farming principles”. Adoption of more regenerative farming practices is growing steadily, but for many farmers, the key question surrounds the financial viability of their adoption when margins are so tight. A recent report commissioned by the Farming for Carbon and Nature Group and funded by the Natural England Environment Investment Readiness Fund (NEIRF) sets out the financial and climate impact of adoption of more regenerative farming practices and systems and includes partial budget information on the financial impact of adoption in England with support from SFI where relevant.
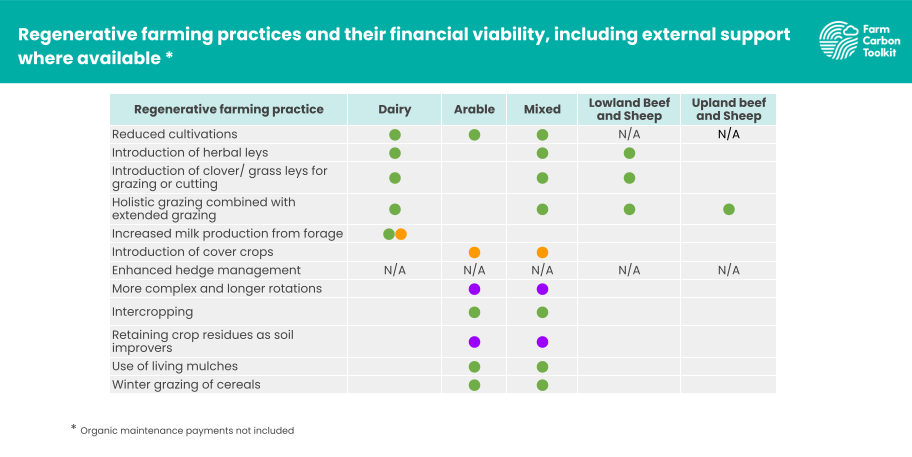
This chart clearly shows that with the inclusion of SFI support, many of the practices generally considered to be regenerative are likely to deliver a similar margin than more conventional practices in these areas. The area where more support is needed is in the adoption of more complex arable rotations including pulses and fertility building leys, where even with appropriate SFI payments, the margins from shorter more degenerative rotations are likely to be more profitable. We are a member of the Nitrogen Climate Smart Consortium which is supporting the increased production of pulses and legumes in the UK together with their use as animal feeds to address the need to reduce the use of artificial fertilisers and imported animal feedstuffs. This project will support farmers to do this through farmer field trials as well as the introduction of new technology for on-farm pulses processing. You can find out more about this project and get involved by following this link.
In summary, I am fairly confident that UK agriculture can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 10% through the adoption of low-carbon farming practices. Indeed through some of the practical work with farmers in which FCT is involved, we are seeing higher levels of emission reductions being achieved within businesses with little or no change in farm output and in many cases increased profitability and business resilience. The element which is mostly missing is the confidence and knowledge to make the necessary changes and knowing where to start.
At FCT we provide a (free for farmers and growers) Farm Carbon Calculator to allow businesses to understand their starting point, a set of tools within our Toolkit to assist businesses to make those chances and a team of expert advisors to talk to.
You can always make contact with us by email [email protected] or by calling us on 07541 453413. We look forward to hearing from you.

















Recent Comments