

by Liz Bowles, CEO
The regenerative sector must unite to offer the government practical solutions, not more problems, to the challenges facing the country.
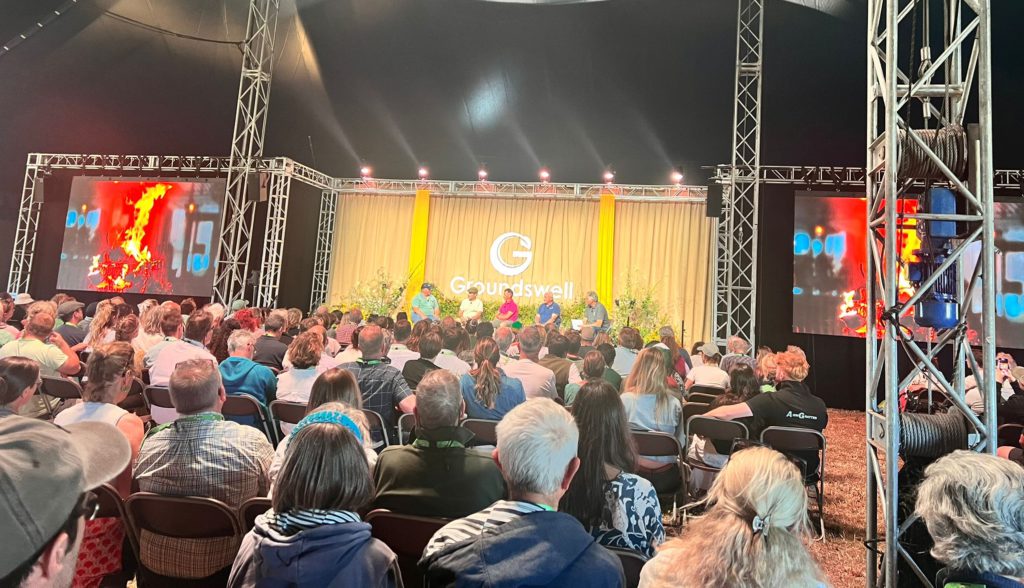
Having been part of Groundswell since its very beginning in 2016, this year’s festival-cum-agricultural event felt more relevant than ever. It was a powerful reminder of the trust, collaboration, and creativity needed to navigate the challenges ahead for UK agriculture.
As CEO of Farm Carbon Toolkit, one of the most rewarding ‘takeaways’ was the recognition that farmers and supply chains alike hold Farm Carbon Toolkit (and our staff) in such high regard because of the trust we’ve built over the many years as a farmer-led and fiercely independent organisation, driven by sound science.
That trust is critical now, and it will be even more important in the years ahead if we are to create food production systems that are resilient, profitable, and nature-friendly in the face of the growing climate crisis. We remain as committed as ever to supporting farmers, growers, and other food businesses to measure, understand, and act on their greenhouse gas emissions, while improving their business resilience through supporting farmers on new practice implementation in areas such as soil health, farm nutrient use efficiency, reducing reliance on artificial nitrogen, agroforestry etc.
Solutions… not more problems
For me, one of the key themes from Groundswell 2025 was the consensus around the need to approach the challenges we face with ‘network thinking’ — collaborating more effectively, creating more circular food systems, ensuring the businesses making changes on the ground have the resources and recognition they deserve, and working together to present a clear, consistent message to the government, whatever colour that might be.
At one excellent session, brilliantly chaired by Sue Pritchard from the Food, Farming and Countryside Commission, it became clear that the regenerative sector must work together to present the government not with more problems, but with practical solutions to the issues the country faces. This solutions-focused approach sits at the very heart of what we do at Farm Carbon Toolkit — providing farmers and growers with practical tools and support to meet our common challenges head-on.
Once the regenerative sector shows how our principles and practices can help the government solve many of its challenges, we can gain real traction and turn ideas into action. At the moment, however, I’m not sure we’re yet thinking in this way — and certainly not with the coherence and strength of voice we need.
FCT and Groundswell: Growing Together
It was also striking to reflect on just how far both Groundswell and Farm Carbon Toolkit have come. When the Groundswell festival first took place in 2016, it was held in the Cherry family’s farmyard with a handful of exhibitors running practical demonstrations outside. We held our very first Soil Farmer of the Year awards ceremony in the grain store!
Since then, Groundswell has grown into one of the largest and most important festivals of regenerative farming in Europe, and FCT has grown alongside it. Back then, we were a team of just one, the inimitable Becky Willson. Today, we’re over 20 strong, working with farmers, growers, producer groups, processors and retailers across the UK and beyond.
Our Farm Carbon Calculator continues to go from strength to strength and is now used on four continents, supporting farmers and growers to understand how they can play their part in reducing greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining productive, climate- and nature-friendly farms. We remain committed to our mission as a Community Interest Company and have recently strengthened our independence by becoming an Employee Ownership Trust.
Facing the Challenges Ahead
We are entering some of the most challenging times our food production systems have ever faced. Climate change is reshaping our weather patterns, with hotter, drier summers, unpredictable and often intense weather events, and increasing pressure on farmers and growers to produce in a more environmentally friendly way.
At Farm Carbon Toolkit, we remain driven by science — not by fashion or the latest trends, however tempting that might sometimes be — and we aim to provide practical support and tools to help farmers and growers navigate this complex and changing landscape.
Some are suggesting that Groundswell is moving away from its farmer-to-farmer roots, becoming more of a stage for those wanting to tell farmers what to do. I didn’t have much time to reflect on that myself. We were busy throughout, speaking to farmers and growers and sharing ideas with friends old and new, all trying to make sense of this evolving landscape together.
But what stood out most was the collective sense that trust, collaboration, and clear, solutions-focused thinking will be essential if we are to meet the challenges ahead of producing the quality and quantity of food we need in a profitable and nature-friendly way.





















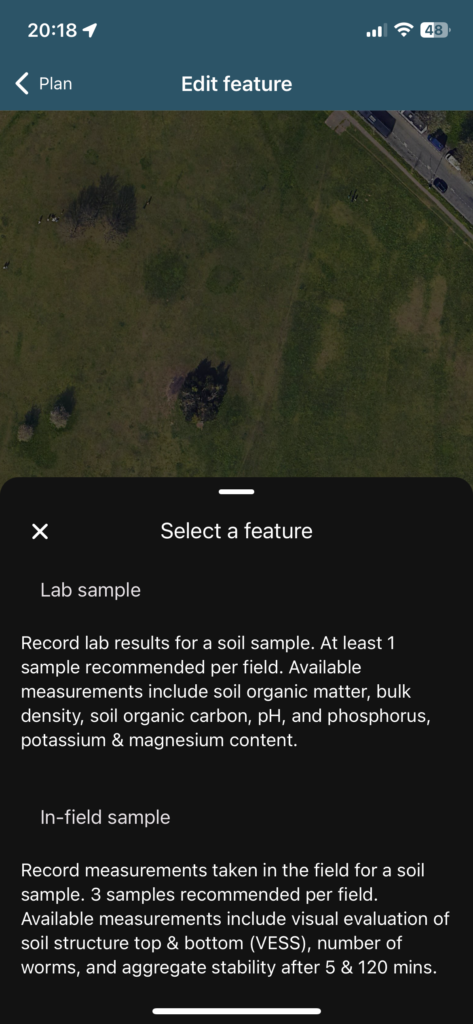
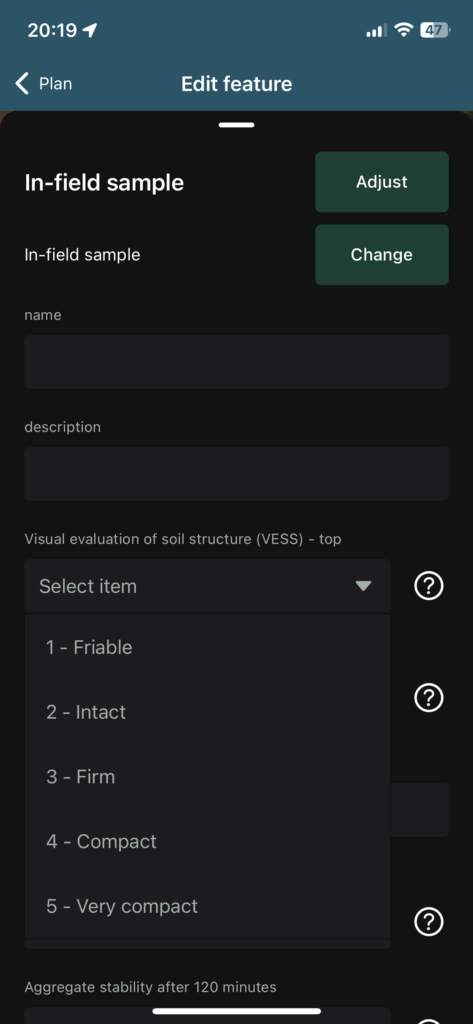
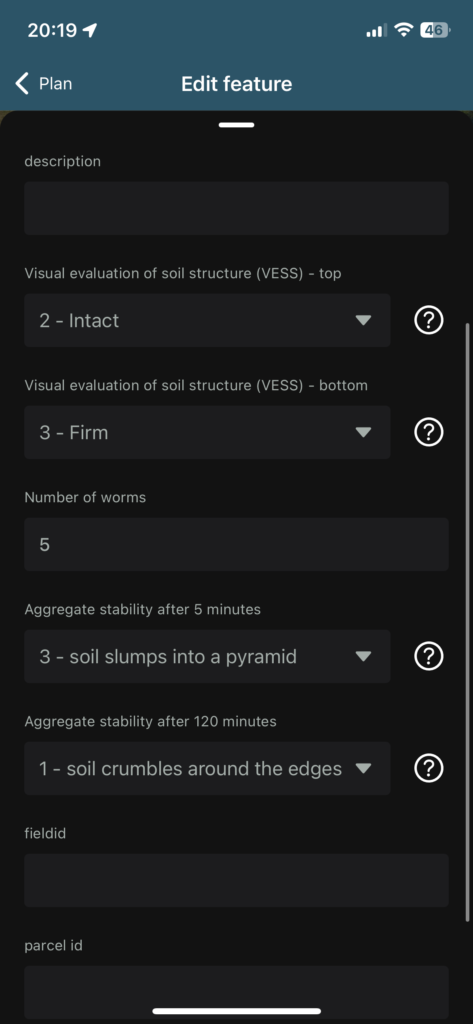








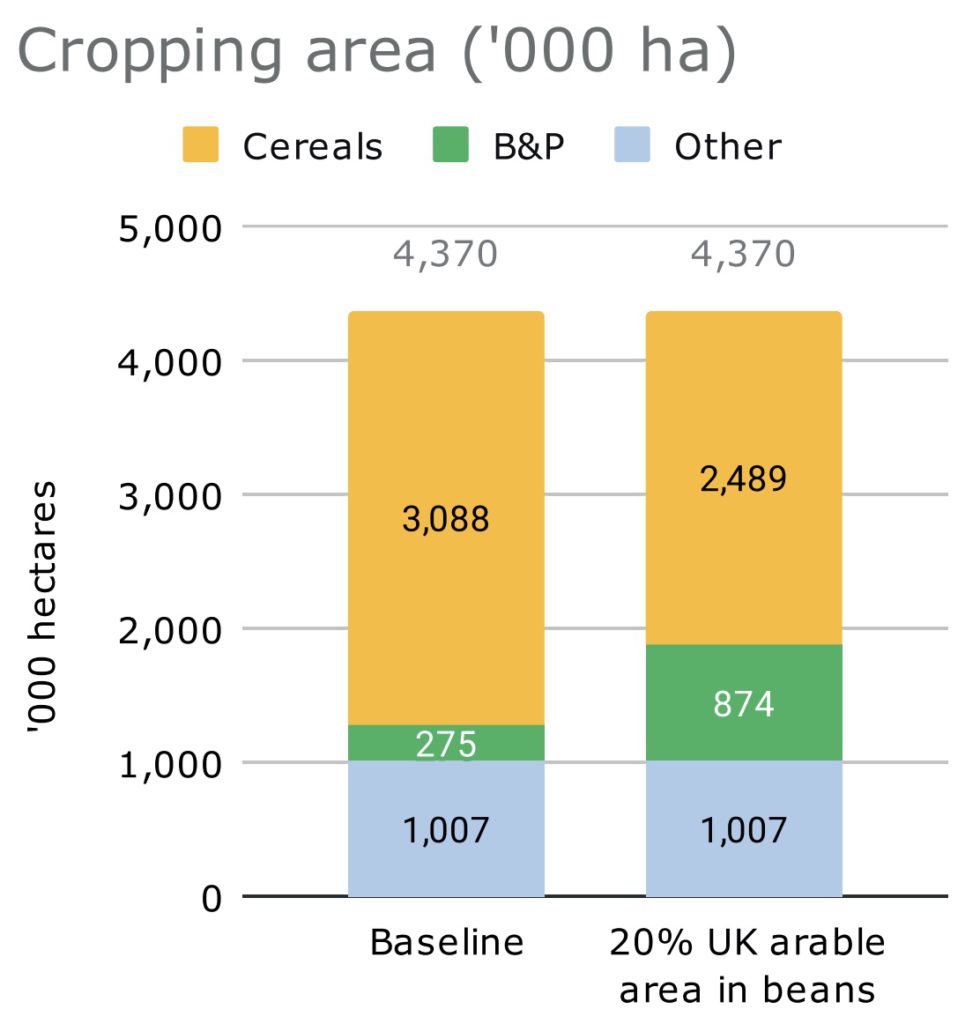
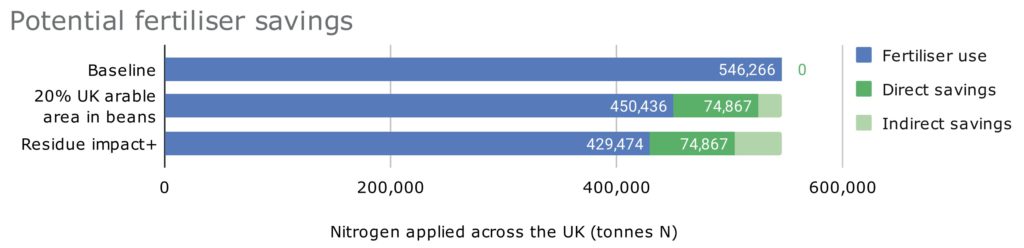
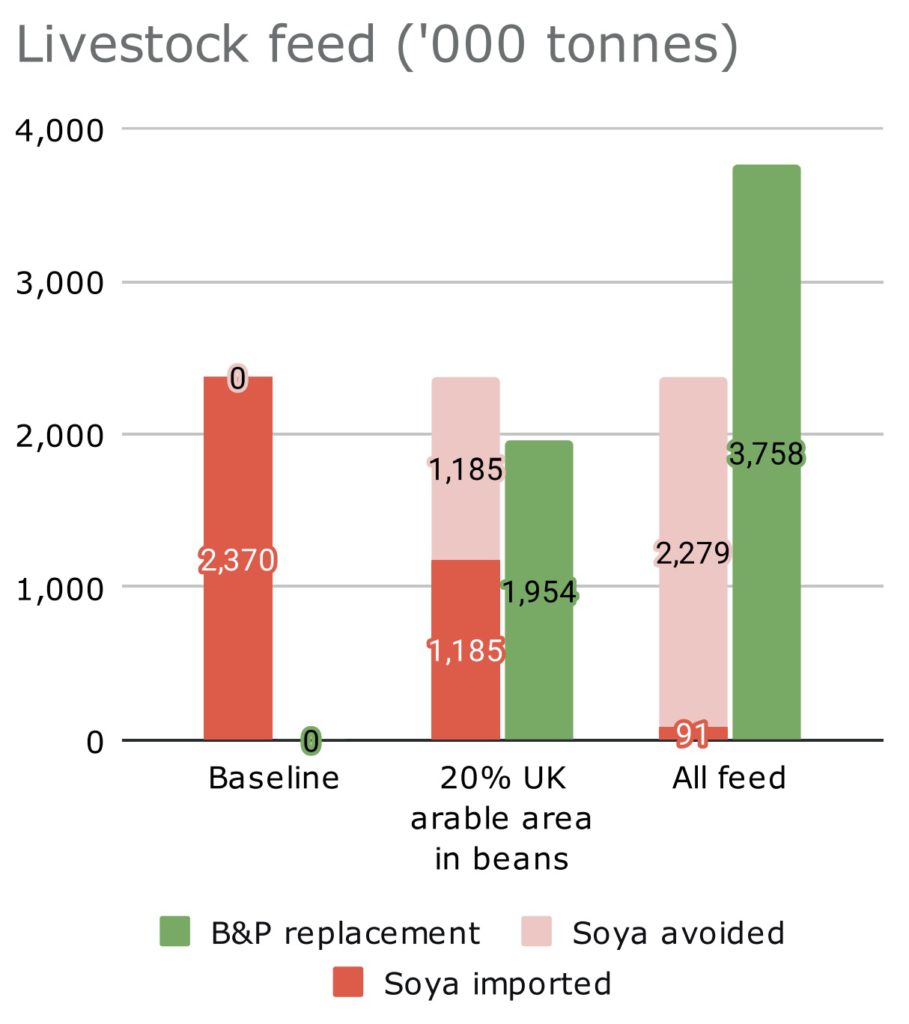
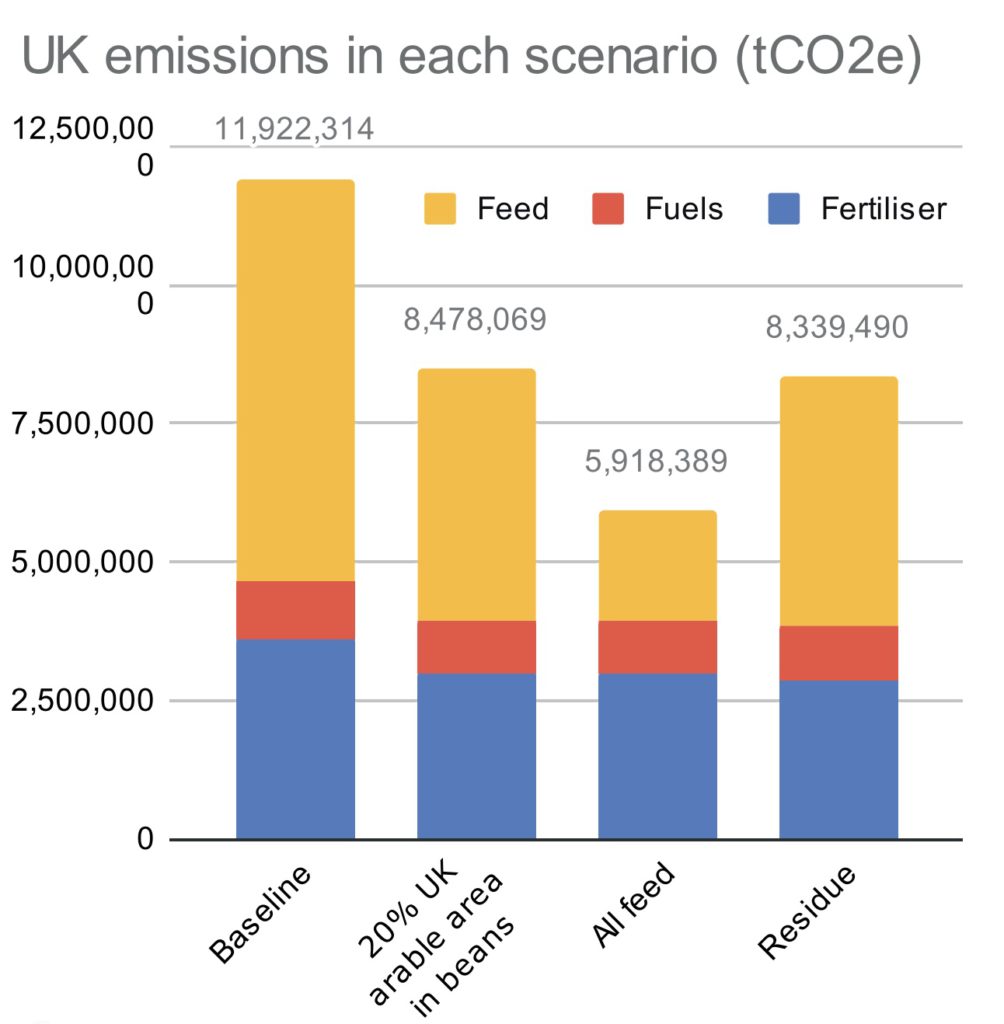














Recent Comments